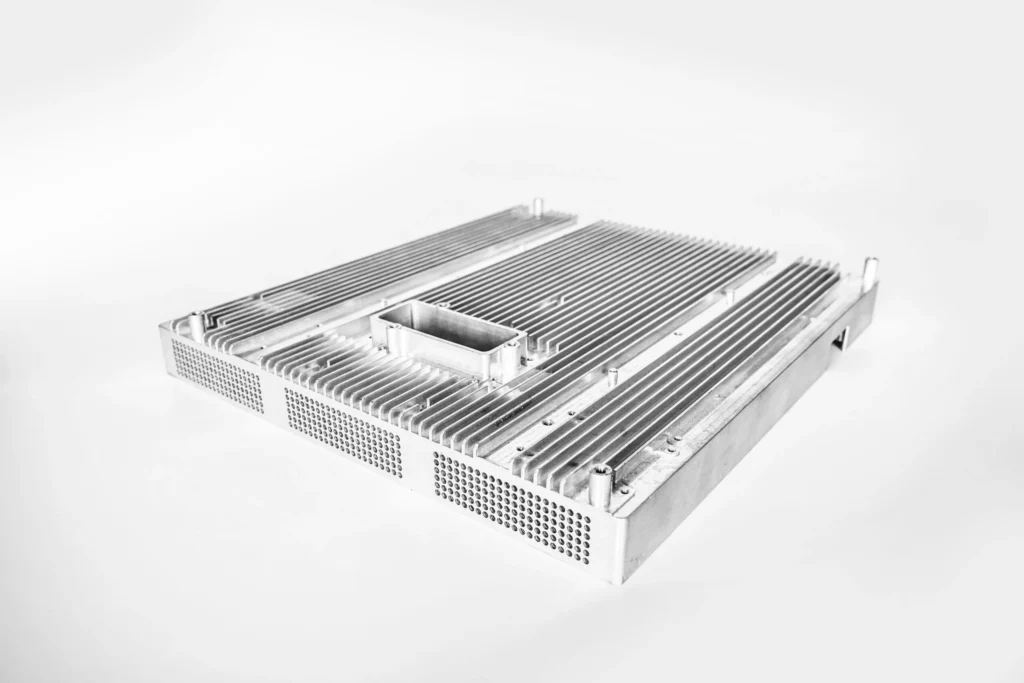
In today’s tech-driven society, it’s crucial to keep devices cool to ensure optimal performance. If devices overheat, they can slow down, or even fail. This is where die cast heat sinks play a role. They help regulate the temperature of high-performance electronics, ensuring operation and longevity. This article delves into the definition of die cast heat sinks, their functionality, and their significance across industries.
Understanding Die Cast Heat Sinks
A die cast heat sink is a device designed to manage heat in gadgets. It involves pouring metals like aluminum or copper into molds to create specific shapes. The primary function of a heat sink is to draw heat from components like CPUs and release it into the surrounding air, preventing overheating and maintaining efficient device operation.
A. Fundamentals of Die Casting
Die casting is a manufacturing technique that involves injecting metal at high pressure into molds to achieve intricate shapes with precision. Die cast heat sinks are renowned for their thermal efficiency and durability.
B. Comparison to Types of Heat Sinks
Various heat sink varieties offer distinct benefits. Die cast heat sinks, in contrast to extruded, heat pipe, forged, and skived types, provide construction and the ability to be shaped intricately. These features make them well suited for demanding applications that prioritize space and efficiency.
The Die Casting Procedure
A. Overview of Die Casting
The die casting process involves stages:
- Metal Melting: Aluminum or copper is typically melted in a furnace.
- Metal Injection: The molten metal is forcefully injected into a mold or die.
- Cooling: The metal rapidly solidifies within the mold.
- Heat Sink Ejection: Once solidified, the part is removed from the mold, with any excess material being trimmed.
B. Materials Utilized in Die Cast Heat Sinks
- Aluminum: Aluminum stands out as a choice for die cast heat sinks due to its lightweight nature, good thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness.
- Copper: Copper boasts thermal conductivity, making it suitable for cooling applications that demand high performance; however, it is heavier and more costly than aluminum.
C. Advantages of Die Casting in Manufacturing Heat Sinks
- Precision and Consistency: Die casting enables the creation of heat sinks with precise measurements and consistent quality, vital for demanding applications that require top performance.
- Intricate Shapes: The die casting method can fabricate heat sinks with designs not achievable by other production techniques, maximizing surface area for optimal heat dissipation.
- Cost Effectiveness for Large Scale Manufacturing: Die casting proves to be a cost-effective approach for producing heat sinks in bulk, catering to industries needing substantial quantities of efficient cooling solutions.
Design Considerations for Die Cast Heat Sinks
A. Thermal Conductivity and Performance
Selecting the right material plays a key role in enhancing thermal conductivity. Aluminum is a choice due to its performance-cost balance, while copper is preferred for applications demanding superior thermal efficiency.
B. Surface and Fin Design
The surface area of a heat sink significantly impacts heat dissipation. Fins are incorporated to increase surface area, facilitating the transfer of heat from electronic components to the ambient air.
C. Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance gauges a heat sink’s ability to conduct heat efficiently. Lower thermal resistance equates to better performance. Engineers design heat sinks to reduce resistance and enhance cooling efficiency.
D. Integration with Thermal Management Components
Heat sinks often collaborate with thermal interface materials (TIMs) and cooling fans to improve cooling effectiveness. Ensuring proper interaction between these components is crucial for efficient thermal management.
Applications of Die Cast Heat Sinks in Various Industries
Die cast heat sinks find applications across various industries for cooling electronic components. Here are some examples:
A. Energy Storage
In energy storage systems, heat sinks help regulate the heat produced by batteries and other components, ensuring safety and optimal performance.
B. Solar Inverters
Solar inverters convert DC power from panels into AC power. Heat sinks aid in cooling these devices, preserving their efficiency and longevity.
C. Automobiles
Modern vehicles house numerous electronic systems that generate heat. Heat sinks assist in maintaining the coolness of these systems, guaranteeing performance.
D. Computer Servers and Data Centers
Servers and data centers emit significant heat. Die cast heat sinks manage this heat effectively, preventing overheating and sustaining peak performance levels.
E. Artificial Intelligence and Telecommunications
AI and telecommunication equipment necessitate efficient cooling mechanisms to handle data processing tasks. Heat sinks play a crucial role in maintaining optimal functioning of these systems.
F. Medical Equipment
In the field of healthcare, essential devices like imaging tools and ventilators rely on cooling systems to maintain their precision and continuous functionality.
Future Trends in Die Cast Heat Sink Technology

A. Advancements in Materials and Design
Ongoing research on materials and sophisticated manufacturing methods is leading to more effective and compact heat sinks. Innovations like graphene and 3D printing show potential for the future.
B. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Heat sinks are now being merged with technologies such as IoT-enabled devices to deliver real-time thermal management and predictive maintenance capabilities.
C. Focus on Sustainability and Environmental Impact
With industries moving towards eco-friendly solutions, sustainable manufacturing practices and the use of recyclable materials are gaining traction in the production of heat sinks.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a die cast heat sink?
A die cast heat sink is a device created by pouring metal into a mold to form a specific shape that aids in dissipating heat from electronic devices.
2 How does a die cast heat sink function?
Die cast heat sinks function by transferring heat from components to the surrounding air, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
3. Which materials are typically utilized for die cast heat sinks?
Aluminum and copper are commonly chosen for their thermal conductivity.
4. What are the benefits of employing die cast heat sinks?
They offer cost-effectiveness, flexibility in design, and efficient thermal capabilities.
5. How do die cast heat sinks stack up against other types of heat sinks?
Compared to other options, die cast heat sinks are often more budget-friendly and versatile; however, they may not match the thermal efficiency of premium solutions like vapor chambers.
6. Which industries frequently rely on die cast heat sinks?
Various sectors such as energy storage, solar power, automotive, computing, artificial intelligence (AI), telecommunications, and medical equipment extensively use die cast heat sinks.
7. Is it possible to customize die cast heat sinks for specific applications?
Indeed, die cast heat sink designs can be customized to cater to specific thermal management requirements.
8. What are the critical factors to consider in designing die cast heat sinks?
Key design considerations include thermal conductivity, surface area optimization, fin design efficiency, and compatibility with other thermal management components.
9. How does the die casting process affect the performance of a heat sink?
The process of die casting enables the creation of precise shapes and sizes, which ultimately improves the thermal efficiency of heat sinks.
10. What are the current advancements in die cast heat sink technology?
Recent trends include advancements in materials, integration with smart technologies, and a focus on sustainable manufacturing practices.
11. What kinds of die cast heat sinks does PTHeatsink manufacture?
PTHeatsink offers a range of customized die cast heat sinks tailored to meet the needs of various industries and applications.
12. How does PTHeatsink ensure the quality of its die cast heat sinks?
Quality is maintained through rigorous testing, inspection procedures, and strict adherence to high manufacturing standards.
13. What is the typical turnaround time for ordering a custom die cast heat sink from PTHeatsink?
Lead times can vary depending on design complexity and production volume. For specific timelines, it is best to contact PTHeatsink directly.
14. How does PTHeatsink assist clients throughout the design and manufacturing phases?
PTHeatsink provides support from initial design concepts to full-scale production, ensuring clear communication
